Salt bridge

The post was last updated on 2022-02-25.
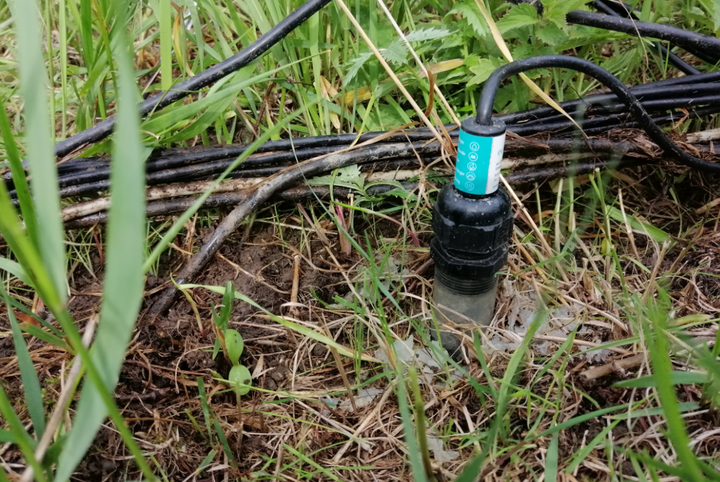
When measuring EH in soils electrons flow from the platinum tipped electrode towards the reference electrode (reducing conditions; high e- activity close to the Pt surface) or vice versa (oxidizing conditions; low e- activity close to the Pt surface). This requieres that the electrical circuit is closed and that both electrodes have a proper contact to the soil matrix. A proper contact of the reference electrode with the soil matrix is important because in order to maintain charge balance within the electrolyte solution of the reference electrode, ions are capable to diffuse outside and inside a porous ceramic diaphragm into the soil. If the contact is disrupted, the release of ions is hampered and a potential might build up or the measured values become erratic. Since the the electrolyte solution is typically a potassium chloride (KCl) solution of variable molarity, K+ ions diffuse outside the electrode when the EH is positive and Cl- ions when the EH is negative (see sketch below).
, adapted from Fiedler et al. 2007; Reddy and DeLaune 2008; Strawn et al. 2015](04.png)
Figure 1: Scheme for measuring redox potentials. Source: Dorau, 2016, adapted from Fiedler et al. 2007; Reddy and DeLaune 2008; Strawn et al. 2015
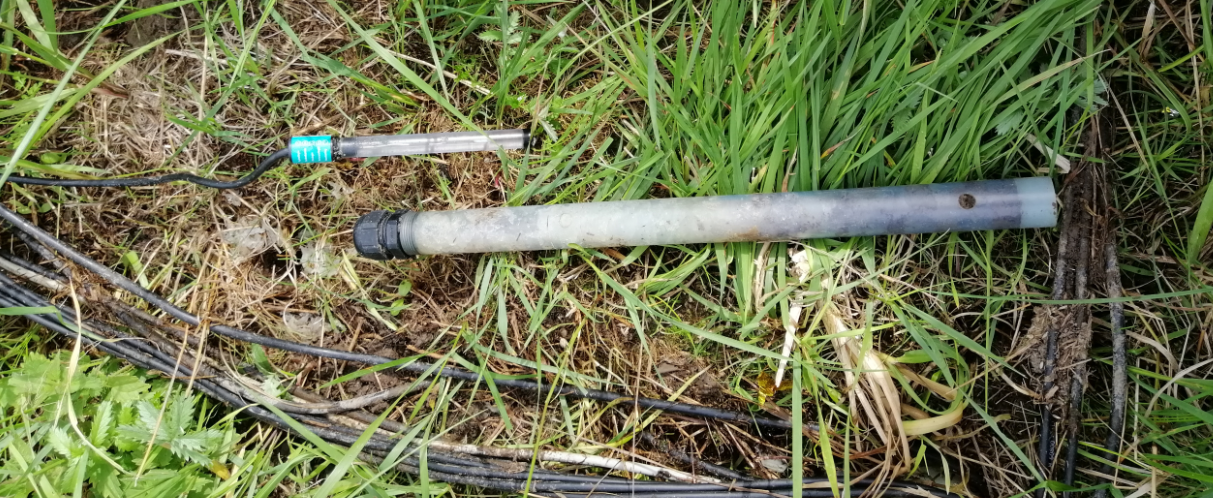

Figure 2: PVC salt bridge filled with a 3 M KCl agar gel with the smaller reference electrode at the side.
📚 Literature recommendation is the chapter about measuring redox potentials in soils from Tim which gives a very detailed overview. Field Measurement Methods in Soil Science
The main advantage of a salt bridge is to (i) extent the lifetime and (ii) applicability under dry soil conditions of the reference electrode. When the reference electrode is placed inside the agar gel within the salt bridge, the internal reference electrode electrolyte remains stable for a longer time since leaching is slowed down and under dry soil conditions the larger surface of the salt bridge is better conductive, thus, the migration of ions (K+ or Cl-) is not disrupted.
Technical problems with EH measurements in soils are known for a long time and therefore recommendations to use a salt bridge date back a long time ago, e.g., the study by Veneman and Pickering (1983). The body consists of a PVC tube with holes in some depths. The salt bridge is typically 30 to 50 cm long and extents into the subsoil, where soil water contents are higher and a better electrical contact is achieved. The PVC tube is then filled with a saturated KCl solution (350 g L-1), heated and by adding agar solution becomes thick forming a gel during cooling. The reference electrode is then pushed inside the gel and voila… the electrical circuit between the reference electrode - KCl gel - soil is closed.
❗ Use of a salt bridge has advantages than simply pushing the reference electrode directly into the soil.
From time to time (maybe every year or biannual), the agar gel needs to be renewed because solubilisation and evapotranspiration foster shrinkage of the gel and under worst conditions the reference electrode hangs in the air. The result would be erratic and faulty EH readings. Below is an example of EH data before and after maintenance of the agar gel inside the salt bridge.
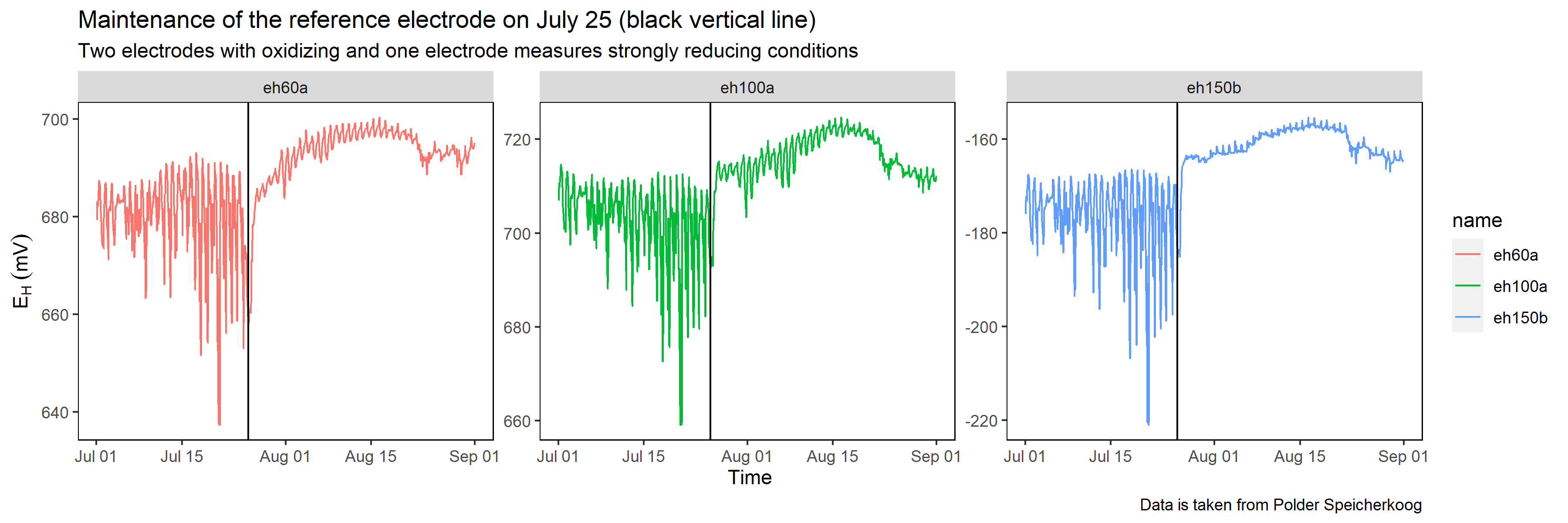
Figure 3: Please note the effect of maintenance when the agar gel is refreshed. The diurnal redox amplitude is drastically smaller.
Directly after renewal of the agar gel diel EH (ΔEH = daily EHmax - daily EHmin) was drastically smaller, indicating that a diel pattern is likely not the consequence of a microbial related pattern - as some authors propose - rather it is technical related noise being present in the data.
🔍 “Redox measurements should not be considered a routine determination and cautious handling of EH data by physical sound corrections is urgently needed…” (More information about the impact of soil temperature on diel EH can be found in our recent article: Dorau et al. 2022, Temperature-induced diurnal redox potential in soil.
The salt bridge is certainly one part of a difficult puzzle to carefully measure EH in soils and obtain reliable data.